Implications Of Sarcopenia On Health And Longevity
It is easy to assume that losing some strength is a “normal part of aging”. In fact, maybe you have even heard this from your healthcare providers. The truth is that getting “weaker” as we age is not “normal” and could be a sign of other medical conditions. Sarcopenia is an “abnormal” loss of muscle mass that must be managed in order for you to live your BEST life well into late adulthood.
In this article, we will go into what sarcopenia is, and things you can start doing today to make sure you avoid this potentially life altering condition.
What Is Sarcopenia?
We gradually lose muscle mass—and strength and function along with it—after we hit 30, seeing a reduction anywhere between 3-8% every decade.
Some lose it more quickly than others, falling prey to sarcopenia.
Sarcopenia is a type of muscle atrophy that comes with the aging process, most commonly affecting people over the age of 60. It can compromise your musculoskeletal system, making you susceptible to frailty, falls, and fractures, increasing your need for institutionalization and hospitalizations, and increasing your risk of mortality.
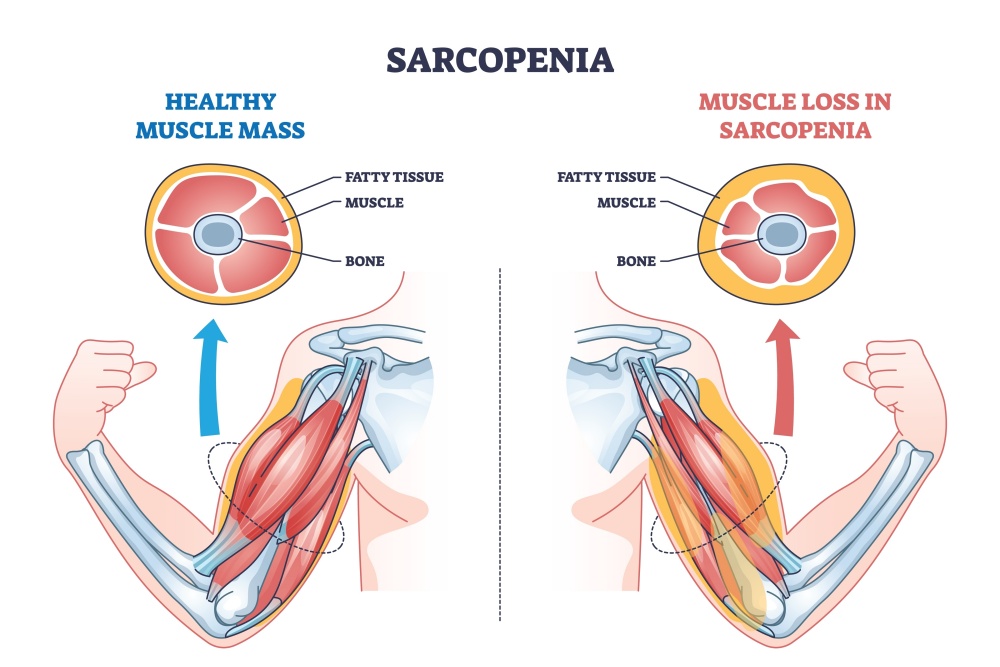
In addition to causing you to spend $860-$933 extra on healthcare (on average), it can also affect your ability to perform everyday tasks like climbing stairs and lifting objects. Thus, it can lead to a loss of independence, impacting your quality of life.
How many older adults have Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is reported to influence the health of up to 16% of older adults over the age of 65%
What Causes Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is an age-related condition, but researchers believe it can also happen due to a sedentary lifestyle, where individuals get little to no physical activity. However, as physically active people also develop sarcopenia, other factors may be at play.
These may include:
- A decline in your body’s ability to synthesize protein (anabolic resistance) to energy, leading to a progressive reduction in muscle mass.
- A reduction in nerve cells, particularly ones responsible for carrying messages from your brain to allow muscles to move.
- Chronic illnesses, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),
- A reduction in hormone levels, such as testosterone, human growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor.
- Not getting adequate nutrition to sustain muscle mass.
Symptoms Of Sarcopenia
People with sarcopenia may experience the following symptoms:
- A reduction in muscle size
- Loss of stamina/endurance
- Poor balance, which can make them susceptible to falls
- Trouble climbing stairs
- Weakness
They also have difficulty doing physical activities, which can further contribute to muscle mass loss. The loss of muscle mass is linked to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. As a result, it can increase fat mass accretion due to low total energy expenditure, making you more susceptible to obesity, diabetes, and hypertension.
So, if you are experiencing these symptoms, instead of treating them as “a normal part of aging”, take a proactive approach, starting with the SARC-F test to assess your risk.
How Is Sarcopenia Diagnosed?
There is no single way to diagnose muscle loss. So, your healthcare provider may start the process by conducting physical tests, such as:
- Chair stand test: It can evaluate leg strength and endurance, especially of the quadriceps. It measures the number of stands a person can complete in 30 seconds without using their arms.
- Handgrip test: This grip power test, which calls for pressing against the dynamometer with all possible force, helps providers identify overall muscle strength. It also tells whether your strength is weakening or just lacking.
- Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB): This objective assessment test combines three different tasks: walking speed, sit-to-stand, and balance, to evaluate lower extremity strength and functioning.
- Timed-Up and Go Test (TUG): TUG measures the time it takes to stand up from a chair, walk 3 meters (10 feet), turn, walk back to the chair, and sit down. This helps assess a person’s mobility, gait, sway, and stability.
- Walking speed test: It measures the speed you walk a specific distance, which can help providers assess your functional mobility.
These physical tests can help evaluate weakness and assess the objective value of muscle function. But in case the provider needs more information to come to a definitive decision, they may recommend imaging tests, such as:
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): It is used to measure fat- and fat-free mass to estimate your true body composition.
- Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA): It is used to determine bone mineral density, which is an accurate way of determining fracture risk.
Sarcopenia Treatment: All You Need To Know
Sarcopenia could result in longer recovery times from injury, and the worst part is that you won’t get back to your pre-injury levels of functioning. It can severely impact your ability to move around, tanking your social life and increasing loneliness.
Seeing that it’s a progressive disease, you must act now to live a long, healthy life.
Treatment for sarcopenia can include:
Physical Activity
Resistance exercise training can enhance muscle mass and strength, making it the first line of defense for managing sarcopenia. You should go over these exercises in a periodized fashion, taking rest periods between sets to optimize the preservation of exercise intensity and meet your training goals.
The best part?
It will also optimize your hormones, which could help minimize sarcopenia symptoms brought on by hormonal changes like menopause.
Diet
Research conducted on 14,585 individuals aged ≥65 years showed that people who ate 4+ servings of fruit had 40% lower odds of sarcopenia. However, it’s important to note that these benefits extended more to women than men.
That said, a well-balanced diet of high-quality protein, fruits, and vegetables could offer protection against muscle wasting, which may treat the effects of sarcopenia.
Medication
While there are no specific medicinal treatments for sarcopenia, recent clinical trials have focused on the following drugs as possible treatment options:
- Growth hormone supplements: They can restore skeletal muscle protein synthesis and lower age-associated oxidative damage, which may combat the development of sarcopenia.
- Testosterone supplements: A high dose of testosterone could reverse age-related sarcopenia by stimulating cellular metabolism and survival pathways.
- Urocortin II (stresscopin-related peptide): It prevents loss of skeletal muscle mass in normal and atrophying muscles.
Something to remember: These studies are conducted on animal subjects, not humans, so more research is required to back their efficacy on Homo sapiens.
Other treatments under the radar include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, which could prevent mitochondrial decline and improve muscle metabolism.
- β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB), which could improve lean muscle mass, strength, and function.
- Vitamin D, which could improve muscle strength and mass.
Apart from these, medications for treating metabolic syndromes may also work—but only when used with resistance training.
In Conclusion
While it’s near impossible to reverse something that has already been brought on by age, you can reduce the severity of the symptoms of sarcopenia by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, and doing resistance-based exercises. This can improve your quality of life, which can, in turn, reduce your risk of mortality overall.
What You Should Know About Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss affects millions of people around the globe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is experienced by almost 20% of the entire population! There are three types of hearing loss, but more than 90% are attributed to sensorineural hearing loss....
A Beginner’s Guide to Tai Chi: Benefits & More
Tai chi, also known as shadow-boxing, is a mind-body exercise developed by the Chinese as a “soft” martial art in the 17th century. This low-impact workout involves slow, intentional movements and deep breaths to achieve a meditative state of mind. It makes you...
Understanding Food Cravings, Their Triggers, and How To Manage Them
We’ve all been beset by food cravings at some point in our lives, but most of us don’t really know where they come from or how to resist them. Since cravings are associated with higher body mass indexes, it has become more important than ever to understand the science...
Want Healthy, Glowing Skin? Try Dry Brushing
Though dry brushing is a comparatively new trend in the skincare world, it has amassed an impressive 130.5 million views on TikTok under a hashtag by the same name. Gwyneth Paltrow and Miranda Kerr are fans of the beauty ritual which speaks of its popularity. As for...
Why You Should Laugh Your Way to Health
The quote, “Laughter is the best medicine,” has more truth to it than you realize. Humor skills or habits—having a propensity to laugh, the enjoyment of humor, the ability to laugh at oneself—are some of the main signature strengths one can possess. In fact, the...
Volunteering: How Helping Others May Impact Overall Health
Volunteering is a pro-social behavior. It’s dedicating your time, attention, and resources toward helping people who are facing hardships in your community with no expectation of any reward or compensation. But there is something in it for you after all. Volunteering...
The Unseen Connection: Oral Health’s Surprising Impact on Heart Health
Did you know that the benefits of maintaining oral health go beyond your mouth? Oral health—the health of your teeth, gums, alveolar bone, etc.—plays a more significant role than you think. Sure, it keeps your gums and teeth clean and healthy. It also helps with basic...
Whispers to Wonders: Unraveling the allure of ASMR
You may have come across the term “ASMR” at least once, particularly if you’ve been on certain corners of social media. Be it TikTok, Instagram, or even YouTube, ASMR videos have been all the rage. Tapping, scratching, whispering, chewing—ASMR (autonomous sensory...
Mind Your Memory: Naturally Nurturing Your Cognitive Strength
Your memory is an intricate tapestry woven with knowledge, experience, and personal history, which forms the cornerstone of human cognition. However, as is the case with any tapestry, your memory will start to wear out with time, and your cognitive health may decline...
Tea-rific Health Benefits of Drinking Green Tea
Around 600,000 tonnes of green tea is consumed annually — a figure that has grown by approximately 20% in the last ten years. When you understand all the benefits of drinking green tea, its popularity isn’t surprising at all. This grassy, flowery, and earthy...











